Instructions on how to connect to a VPN Server by using L2TP/IPsec VPN Client which is built-in on Mac OS X.
Screen-shots are taken on Mac OS X Mountain Lion. Other versions of Mac OS X are similar, however there might be minor differences with UIs.
1. Initial configurations only.
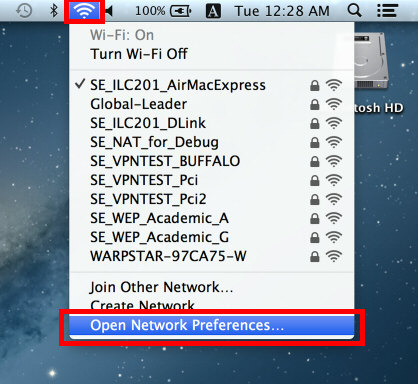
Click the network icon on the top-right side on the Mac screen. Click “Open Network Preferences…” in the menu.
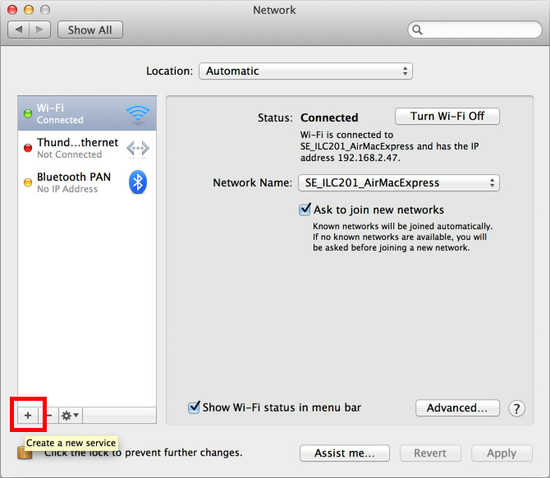
Click the “+” button on the network configuration screen.
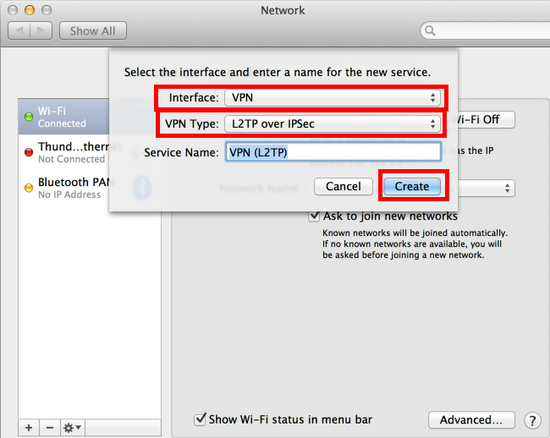
Select “VPN” as “Interface” , “L2TP over IPsec” as “VPN Type” and click the “Create” button.
A new L2TP VPN configuration will be created, and the configuration screen will appear.
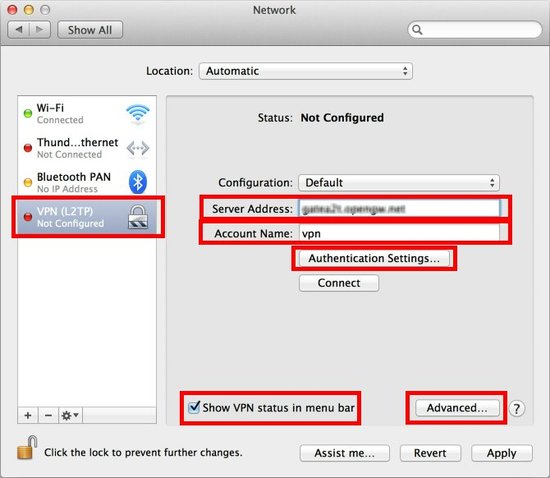
On this screen, you have to specify either hostname or IP address of the destination VPN Server.
After you specified the “Server Address” , input the user-name on the “Account Name” field, which is the next to the “Server Address” field.
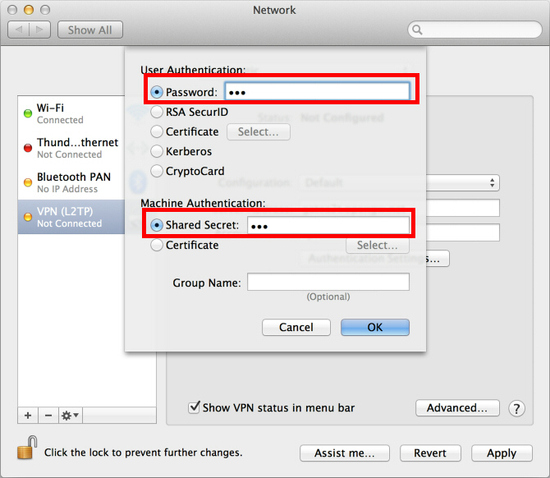
Next, click the “Authentication Settings…” button.
The authentication screen will appear. Input your password in the “Password” field. Specify the pre-shared key also on the “Shared Secret” field. After you input them, click the “OK” button.
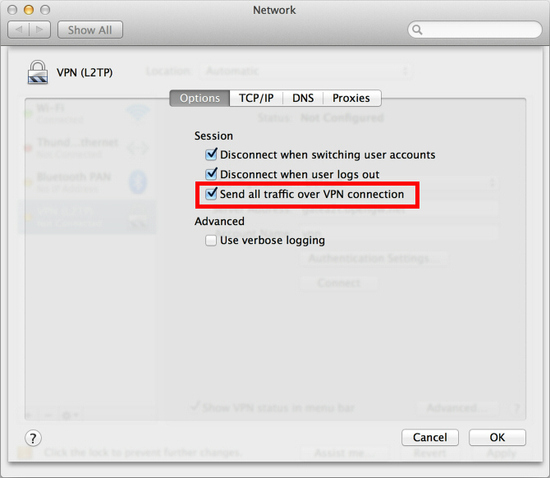
Return to the previous screen, check the “Show VPN status in menu bar” and click the “Advanced…” button.
The advanced settings will appear. Check the “Send all traffic over VPN connection” and click the “OK” button.
On the VPN connection settings screen, click the “Connect” button to start the VPN connection.
2. Start a VPN connection
You can start a new VPN connection by clicking the “Connect” button at any time. You can also initiate a VPN connection by clicking the VPN icon on the menu bar.
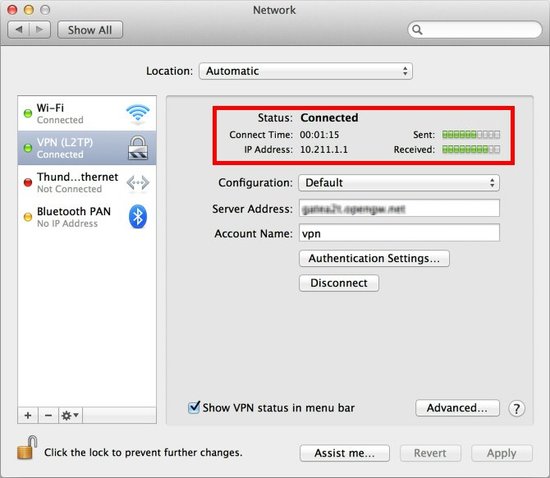
After the VPN connection is established, the VPN connection setting screen will show “Connected”. Your private IP address on the VPN, and connect duration time will be displayed on the screen.
3. Enjoy VPN communication
While VPN is established, all communications will be relayed via the VPN Server. You can access any local servers and workstation on the destination network.